Full Pane: High Latitude Arctic Deep Sea Expedition (Russia 2007)
High Latitude Arctic Deep Sea Expedition (Russia 2007)
07 December (Russia ) within release Arctic Exploration 2007 goes into circulation Full Pane High Latitude Arctic Deep Sea Expedition face value 24*8 Russian ruble
Full Pane is horizontal format.
Label text: During a high-latitude Arctic deep-sea expedition on August 2, 2007, the Russian flag was planted on the bottom of the Arctic Ocean.Full Pane High Latitude Arctic Deep Sea Expedition it reflects the thematic directions:
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design that is used as a symbol, as a signaling device, or as decoration. The term flag is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have since evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is similarly challenging (such as the maritime environment where semaphore is used). National flags are patriotic symbols with varied wide-ranging interpretations, often including strong military associations due to their original and ongoing military uses. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for other decorative purposes. The study of flags is known as vexillology, from the Latin word vexillum, meaning flag or banner.
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or imagined, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the medieval Latin Mappa mundi, wherein mappa meant napkin or cloth and mundi the world. Thus, "map" became the shortened term referring to a two-dimensional representation of the surface of the world.
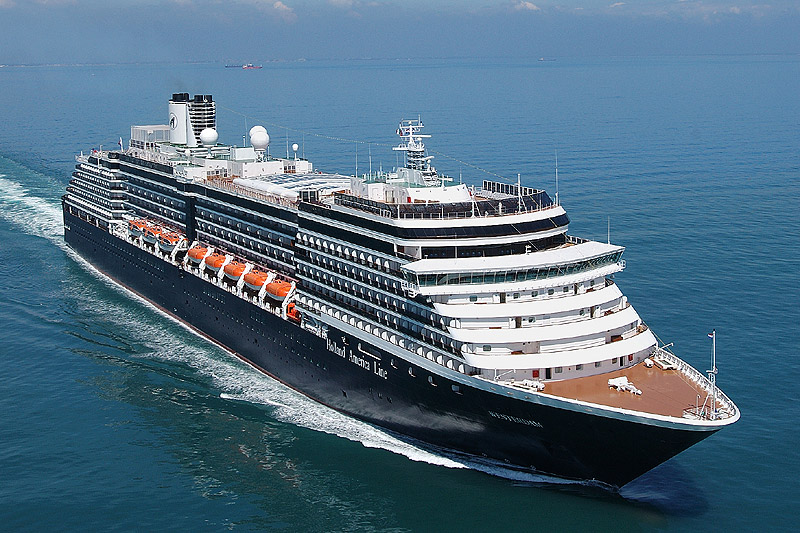
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying passengers or goods, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Historically, a "ship" was a sailing vessel with at least three square-rigged masts and a full bowsprit. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape and load capacity.
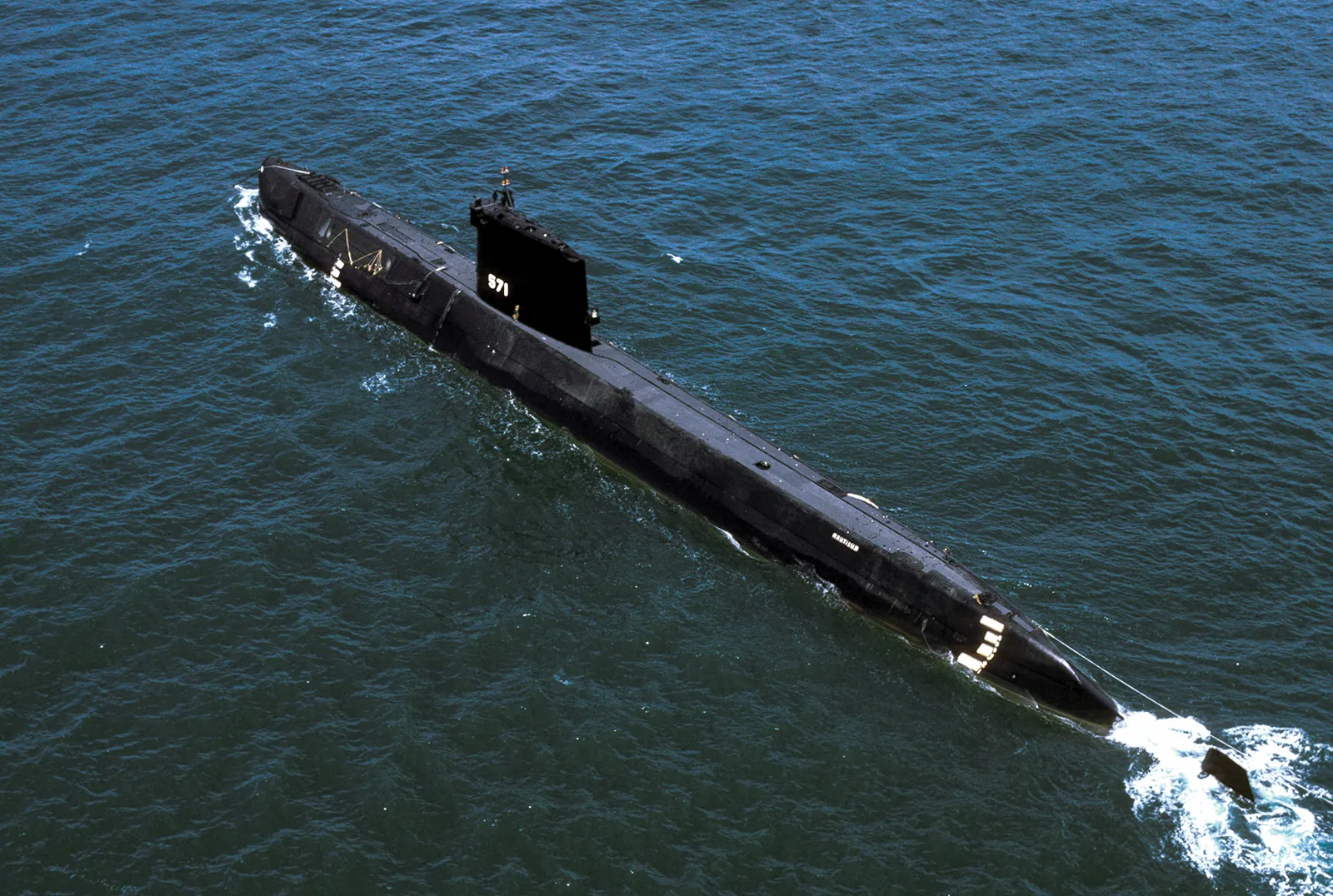
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or informally to refer to remotely operated vehicles and robots, or to medium-sized or smaller vessels (such as the midget submarine and the wet sub). Submarines are referred to as boats rather than ships regardless of their size