Topic

Frescos
Fresco (pl. frescos or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word fresco (Italian: affresco) is derived from the Italian adjective fresco meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting.

Frogs
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura[(coming from the Ancient Greek ἀνούρα, literally 'without tail'). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" Triadobatrachus is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar (250 million years ago), but molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history.

Fruits
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate seeds. Edible fruits, in particular, have propagated with the movements of humans and animals in a symbiotic relationship as a means for seed dispersal and nutrition; in fact, humans and many animals have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Accordingly, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language usage, "fruit" normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of a plant that are sweet or sour, and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. On the other hand, in botanical usage, "fruit" includes many structures that are not commonly called "fruits", such as bean pods, corn kernels, tomatoes, and wheat grains. The section of a fungus that produces spores is also called a fruiting body.

Fruits and Berries
In botany, a berry is a fleshy fruit without a drupe (pit) produced from a single flower containing one ovary. Berries so defined include grapes, currants, and tomatoes, as well as cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), persimmons and bananas, but exclude certain fruits that meet the culinary definition of berries, such as strawberries and raspberries. The berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit in which the entire outer layer of the ovary wall ripens into a potentially edible "pericarp". Berries may be formed from one or more carpels from the same flower (i.e. from a simple or a compound ovary).: 291 The seeds are usually embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary, but there are some non-fleshy exceptions, such as Capsicum species, with air rather than pulp around their seeds.

Funeral services
A funeral director, also known as an undertaker or mortician (American English), is a professional who has licences in funeral arranging and embalming (or preparation of the deceased) involved in the business of funeral rites. These tasks often entail the embalming and burial or cremation of the dead, as well as the arrangements for the funeral ceremony (although not the directing and conducting of the funeral itself unless clergy are not present). Funeral directors may at times be asked to perform tasks such as dressing (in garments usually suitable for daily wear), casketing (placing the corpse in the coffin), and cossetting (applying any sort of cosmetic or substance to the best viewable areas of the corpse for the purpose of enhancing its appearance) with the proper licences. A funeral director may work at a funeral home or be an independent employee.

Furniture
Furniture refers to objects intended to support various human activities such as seating (e.g., stools, chairs, and sofas), eating (tables), storing items, working, and sleeping (e.g., beds and hammocks). Furniture is also used to hold objects at a convenient height for work (as horizontal surfaces above the ground, such as tables and desks), or to store things (e.g., cupboards, shelves, and drawers). Furniture can be a product of design and can be considered a form of decorative art. In addition to furniture's functional role, it can serve a symbolic or religious purpose. It can be made from a vast multitude of materials, including metal, plastic, and wood. Furniture can be made using a variety of woodworking joints which often reflects the local culture.

Gaelic Football
Gaelic football (Irish: Peil Ghaelach; short name Peil, Ulster Scots: Gaelic fitbaw), commonly known as simply Gaelic, GAA or Football is an Irish team sport. A form of football, it is played between two teams of 15 players on a rectangular grass pitch. The objective of the sport is to score by kicking or punching the ball into the other team's goal (3 points) or between two upright posts above the goal and over a crossbar 2.5 metres (8 ft 2 in) above the ground (1 point).
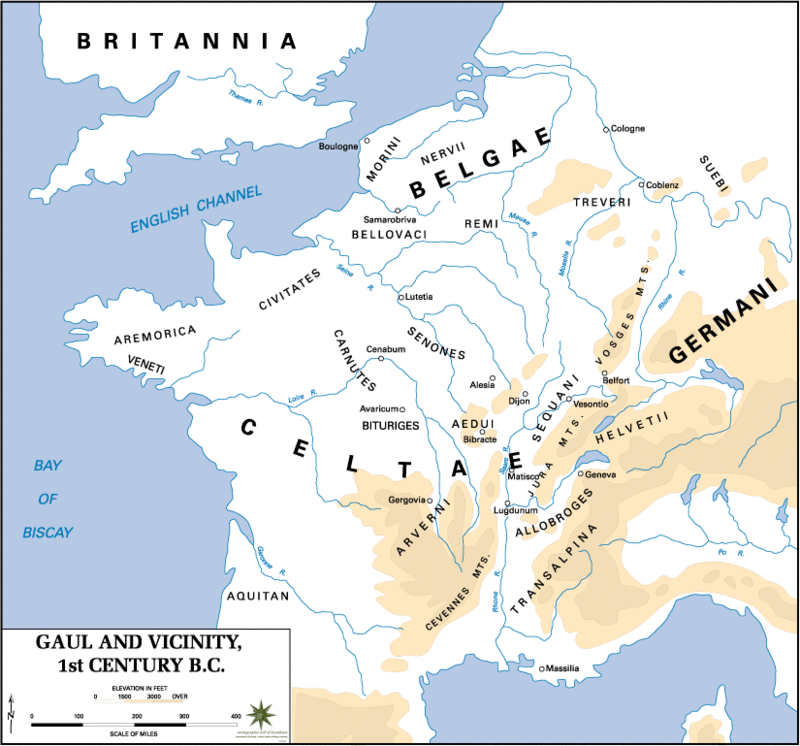
Gallic Era
During the protohistoric period, Brittany was inhabited by five Celtic tribes

Gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of value ("the stakes") on a random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy are discounted. Gambling thus requires three elements to be present: consideration (an amount wagered), risk (chance), and a prize. The outcome of the wager is often immediate, such as a single roll of dice, a spin of a roulette wheel, or a horse crossing the finish line, but longer time frames are also common, allowing wagers on the outcome of a future sports contest or even an entire sports season.

Games and Toys
A toy or plaything is an object that is used primarily to provide entertainment. Simple examples include toy blocks, board games, and dolls. Toys are often designed for use by children, although many are designed specifically for adults and pets. Toys can provide utilitarian benefits, including physical exercise, cultural awareness, or academic education. Additionally, utilitarian objects, especially those which are no longer needed for their original purpose, can be used as toys. Examples include children building a fort with empty cereal boxes and tissue paper spools, or a toddler playing with a broken TV remote control. The term "toy" can also be used to refer to utilitarian objects purchased for enjoyment rather than need, or for expensive necessities for which a large fraction of the cost represents its ability to provide enjoyment to the owner, such as luxury cars, high-end motorcycles, gaming computers, and flagship smartphones.

Gastronomy
Gastronomy is the study of the relationship between food and culture, the art of preparing and serving rich or delicate and appetizing food, the cooking styles of particular regions, and the science of good eating. One who is well versed in gastronomy is called a gastronome, while a gastronomist is one who unites theory and practice in the study of gastronomy. Practical gastronomy is associated with the practice and study of the preparation, production, and service of the various foods and beverages, from countries around the world. Theoretical gastronomy supports practical gastronomy. It is related with a system and process approach, focused on recipes, techniques and cookery books. Food gastronomy is connected with food and beverages and their genesis. Technical gastronomy underpins practical gastronomy, introducing a rigorous approach to evaluation of gastronomic topics

Gears
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called cogs), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit rotational power. While doing so, they can change the torque and rotational speed being transmitted (in inverse proportion) and also change the rotational axis of the power being transmitted. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape

Gears - Cogs Wheels
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or cavities machined on the part, or separate pegs inserted into it. In the latter case, the gear is usually called a cogwheel. A cog may be one of those pegs or the whole gear.Two or more meshing gears are called a gear train.

Geese
A goose (pl.: geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera Anser (grey geese and white geese) and Branta (black geese). Some members of the Tadorninae subfamily (e.g., Egyptian goose, Orinoco goose) are commonly called geese, but are not considered "True Geese" taxonomically. More distantly related members of the family Anatidae are swans, most of which are larger than true geese, and ducks, which are smaller.

Gemstones
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. Certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well.Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability
Genealogy
Genealogy (from Ancient Greek γενεαλογία (genealogía) 'the making of a pedigree') is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives. The field of family history is broader than genealogy, and covers not just lineage but also family and community history and biography