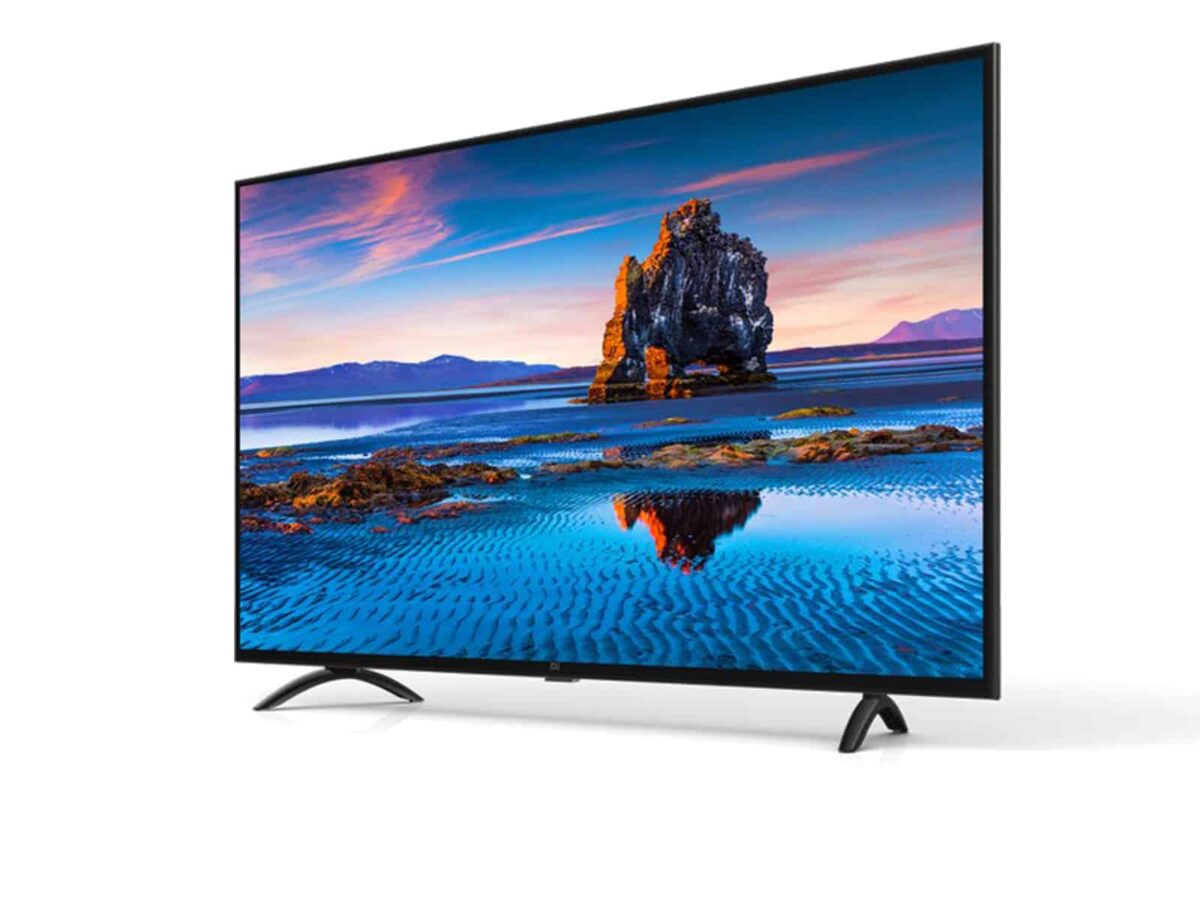
Stamp: Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter (India 1989)
Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter (India 1989)
15 May (India ) within release Science and Technology goes into circulation Stamp Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter face value 40 Indian paisa
| Stamp Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter in catalogues | |
|---|---|
| Stanley Gibbons: | Sg: IN 1212a |
Stamp is square format.
Printed by : Security Printing Press, NasikAlso in the issue Science and Technology:
- Stamp - Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter face value 40;
- Stamp - Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter face value 40;
Stamp Television Set, Dish Aerial and Transmitter it reflects the thematic directions:
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies.
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates oscillating electrical energy, often characterized as a wave. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver, this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe.Modern science is typically divided into two or three major branches: the natural sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology), which study the physical world; and the behavioural sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals and societies.The formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science), which study formal systems governed by axioms and rules, are sometimes described as being sciences as well; however, they are often regarded as a separate field because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method or empirical evidence as their main methodology. Applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. The medium is capable of more than "radio broadcasting," which refers to an audio signal sent to radio receivers.