Stamp: La Reforma palace - 2c on 5c (red) (Guatemala 1912)
La Reforma palace - 2c on 5c (red) (Guatemala 1912)
10 April (Guatemala ) within release Official - 1912 perf issue goes into circulation Stamp La Reforma palace - 2c on 5c (red) face value 2 Guatemalan centavo
| Stamp La Reforma palace - 2c on 5c (red) in catalogues | |
|---|---|
| Colnect codes: | Col: GT O1912-02 |
Stamp is horizontal format.
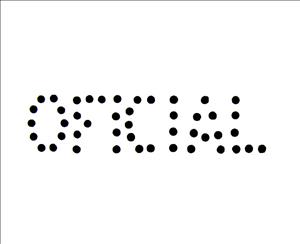
Definitive stamp perforated "OFICIAL" for use on external mail sent from government offices in Guatemala City. The date given here refers to the decree which necessitated these perfins, but in practice they were applied to stamps requisitioned from available stocks, so the actual issue date is approximate. The perfin may exist upright, inverted, reversed and reversed inverted. This stamp was footnoted by Sn in 2009 but not in 2021. Forged perfins may exist.Also in the issue Official - 1912 perf issue:
- Stamp - La Reforma palace - 2c on 5c (red) face value 2;
- Stamp - Lake Amatitlán - 6c on 10c face value 6;
- Stamp - Miguel Garcia Granados (1809-1878), 8th President - 1c on 6c face value 1;
Stamp La Reforma palace - 2c on 5c (red) it reflects the thematic directions:
Architecture (Latin architectura, from the Greek ἀρχιτέκτων arkhitekton "architect", from ἀρχι- "chief" and τέκτων "builder") is both the process and the product of planning, designing, and constructing buildings and other physical structures. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilizations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements.
A building or edifice is a structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, to land prices, ground conditions, specific uses and aesthetic reasons. Buildings serve several needs of society – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the outside (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful).
A museum (/mjuːˈziːəm/ mew-ZEE-əm) is an institution dedicated to displaying and/or preserving culturally or scientifically significant objects. Many museums have exhibitions of these objects on public display, and some have private collections that are used by researchers and specialists. Compared to a library, a museum hosts a much wider range of objects and usually focus around a specific theme such as the arts, science, natural history, local history, and other topics. Public museums that host exhibitions and interactive demonstrations are often considered to be tourist attractions, and many museums attract large numbers of visitors from outside their host country, with the most visited museums in the world regularly attracting millions of visitors annually.
A palace is a large residence, often serving as a royal residence or the home for a head of state or another high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which housed the Imperial residences