Stamp: Sun and observatory (Hungary 1959)
Sun and observatory (Hungary 1959)
14 March (Hungary ) within release International Geophysical Year goes into circulation Stamp Sun and observatory face value 1 Hungarian forint
| Stamp Sun and observatory in catalogues | |
|---|---|
| Philatelia Hungarica Catalog: | PHu: HU 1640Tny |
Stamp is horizontal format.
White spot between "Y" and "A" in MAGYARAlso in the issue International Geophysical Year:
- Stamp - Eötvös Torsion Balance and Globe face value 10;
- Stamp - Deep sea exploration: research vessel and iceberg face value 20;
- Stamp - Icebergs, penguins and polar light face value 30;
- Stamp - Soviet Antarctic camp and map of Pole face value 40;
- Stamp - Space probe approaching moon face value 60;
- Stamp - Sun and observatory face value 1;
- Stamp - Satellite, Sputnik and American Rocket face value 5;
- Stamp - Soviet antarctic camp and map of pole face value 40;
- Stamp - Space probe aproaching moon face value 60;
- Stamp - Sun and observatory face value 1;
- Stamp - Sattelite ,sputnic and american rocket face value 5;
- Stamp - Eotvos Torsion balance and globe face value 10;
- Stamp - Deep sea exploration face value 20;
- Stamp - Icebergs -polar light face value 30;
- Stamp - Deep sea exploration: research vessel and iceberg face value 20;
- Stamp - Deep sea exploration: research vessel and iceberg face value 20;
- Stamp - Deep sea exploration: research vessel and iceberg face value 20;
- Stamp - Satellite, Sputnik and American Rocket face value 5;
- Stamp - Soviet Antarctic camp and map of Pole face value 40;
- Stamp - Space probe approaching moon face value 60;
- Stamp - Sun and observatory face value 1;
- Stamp - Soviet Antarctic Camp and Map of Pole face value 40;
Stamp Sun and observatory it reflects the thematic directions:
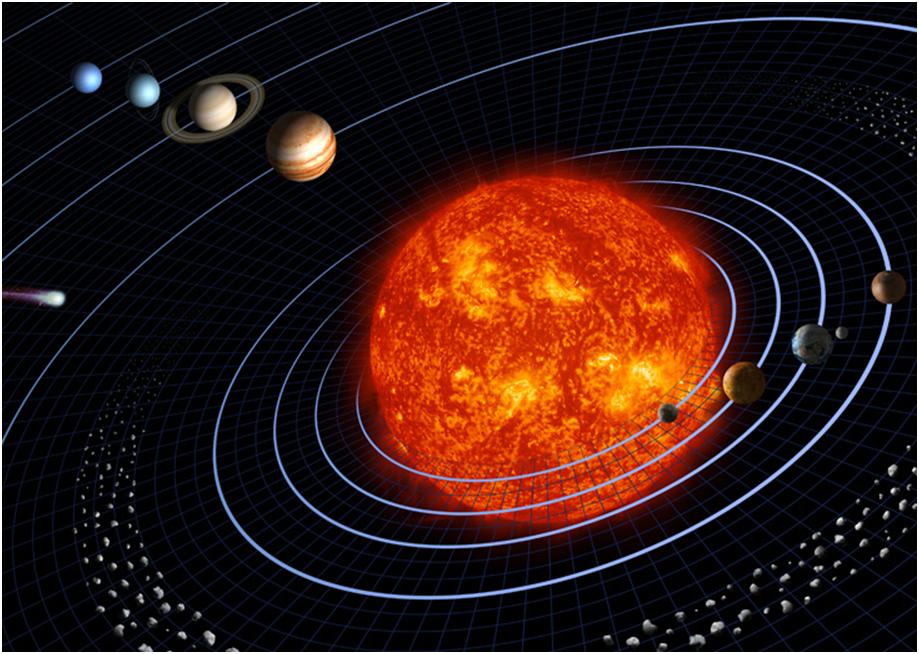
Celestial bodies or heavenly bodies are objects in space such as the sun, moon, planets, and stars. They form a part of the vast universe we live in and are usually very far from us.
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe.Modern science is typically divided into two or three major branches: the natural sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology), which study the physical world; and the behavioural sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals and societies.The formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science), which study formal systems governed by axioms and rules, are sometimes described as being sciences as well; however, they are often regarded as a separate field because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method or empirical evidence as their main methodology. Applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine
The Sun, also known as Sol, is a star at the center of the solar system. It is a white star that gives off different types of energy such as infrared energy (heat), ultraviolet light, radio waves and light. It also gives off a stream of particles, which reaches Earth as "solar wind". The source of all this energy is nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion is the reaction in the star which turns hydrogen into helium and makes huge amounts of energy. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma.