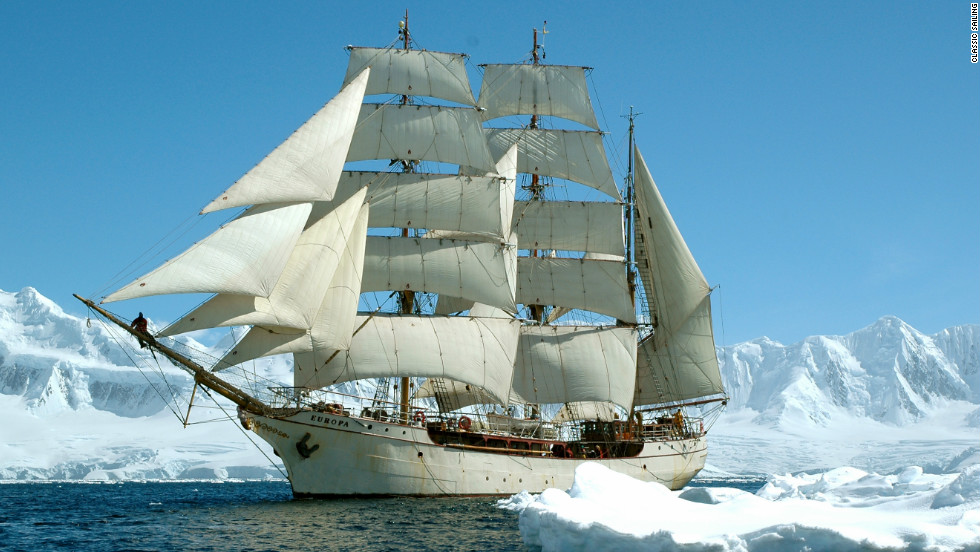
Stamp: Dezhnev's ship and his route (1648) (Soviet Union, USSR 1949)
Dezhnev's ship and his route (1648) (Soviet Union, USSR 1949)
30 January (Soviet Union, USSR ) within release 300th Anniversary of Dezhnev's Discovery of Bering Strait goes into circulation Stamp Dezhnev's ship and his route (1648) face value 1 Russian ruble
| Stamp Dezhnev's ship and his route (1648) in catalogues | |
|---|---|
| Michel: | Mi:SU 1317 |
Stamp is horizontal format.
Also in the issue 300th Anniversary of Dezhnev's Discovery of Bering Strait:
- Stamp - Cape Dezhnev face value 40;
- Stamp - Dezhnev's ship and his route (1648) face value 1;
Stamp Dezhnev's ship and his route (1648) it reflects the thematic directions:
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms and how they integrate with natural or man-made features. A landscape includes the physical elements of geophysically defined landforms such as (ice-capped) mountains, hills, water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds and the sea, living elements of land cover including indigenous vegetation, human elements including different forms of land use, buildings and structures, and transitory elements such as lighting and weather conditions. Combining both their physical origins and the cultural overlay of human presence, often created over millennia, landscapes reflect a living synthesis of people and place that is vital to local and national identity. The character of a landscape helps define the self-image of the people who inhabit it and a sense of place that differentiates one region from other regions. It is the dynamic backdrop to people’s lives. Landscape can be as varied as farmland, a landscape park, or wilderness. The earth has a vast range of landscapes, including the icy landscapes of polar regions, mountainous landscapes, vast arid desert landscapes, islands and coastal landscapes, densely forested or wooded landscapes including past boreal forests and tropical rainforests, and agricultural landscapes of temperate and tropical regions.
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or imagined, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the medieval Latin Mappa mundi, wherein mappa meant napkin or cloth and mundi the world. Thus, "map" became the shortened term referring to a two-dimensional representation of the surface of the world.
Geography (from Ancient Greek γεωγραφία geōgraphía; combining gê 'Earth' and gráphō 'write') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of the Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines
A glacier (US: /ˈɡleɪʃər/; UK: /ˈɡlæsiər, ˈɡleɪsiər/) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water.
A sea is a large body of salty water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the World Ocean, the wider body of seawater. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order sections of the oceanic sea (e.g. the Mediterranean Sea), or certain large, nearly landlocked bodies of water.
A modern sailing ship or sailship is any large wind-powered vessel. Traditionally a sailing ship (or simply ship) is a sailing vessel that carries three or more masts with square sails on each. Large sailing vessels that are not ship-rigged may be more precisely referred to by their sail rig, such as schooner, barque (also spelled "bark"), brig, barkentine, brigantine or sloop. There are many different types of sailing ships, but they all have certain basic things in common. Every sailing ship has a hull, rigging and at least one mast to hold up the sails that use the wind to power the ship. The crew who sail a ship are called sailors or hands. They take turns to take the watch, the active managers of the ship and her performance for a period. Watches are traditionally four hours long. Some sailing ships use traditional ship's bells to tell the time and regulate the watch system, with the bell being rung once for every half hour into the watch and rung eight times at watch end (a four-hour watch). Ocean journeys by sailing ship can take many months, and a common hazard is becoming becalmed because of lack of wind, or being blown off course by severe storms or winds that do not allow progress in the desired direction. A severe storm could lead to shipwreck, and the loss of all hands. Sailing ships are limited in their maximum size compared to ships with heat engines, so economies of scale are also limited. The heaviest sailing ships (limited to those vessels for which sails were the primary means of propulsion) never exceeded 14,000 tons displacement. Sailing ships are therefore also very limited in the supply capacity of their holds, so they have to plan long voyages carefully to include many stops to take on provisions and, in the days before watermakers, fresh water.
An anniversary is the date on which an event took place or an institution was founded in a previous year, and may also refer to the commemoration or celebration of that event. For example, the first event is the initial occurrence or, if planned, the inaugural of the event. One year later would be the first anniversary of that event. The word was first used for Catholic feasts to commemorate saints. Most countries celebrate national anniversaries, typically called national days. These could be the date of independence of the nation or the adoption of a new constitution or form of government. The important dates in a sitting monarch's reign may also be commemorated, an event often referred to as a "Jubilee".